Dramatically Enhanced Visible-Light-Responsive H2 Evolution of Cd1-xZnxS via the Synergistic Effect of Ni2P and 1T/2H MoS2 Cocatalysts
MA Xiao-Wei, LIN Hai-Feng, LI Yan-Yan*, WANG Lei, PU Xi-Peng* and YI Xiu-Jie*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2021, 40, 7-22 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-2752
January 15, 2021
uniform Cd1-xZnxS–Ni2P–MoS2 nano-spheres, MoS2 with 1T/2H mixed-phases, photocatalytic H2 evolution, charge transfer pathways, active sites
ABSTRACT
Photocatalytic hydrogen generation from
water-splitting holds huge promise for resolving the current energy shortage
and environmental issues. Nevertheless, it is still challenging so far to
develop non-noble-metal photocatalysts which are efficient toward solar-powered
hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). In this work, through an ultrasonic
water-bath strategy combined with solvothermal and electrostatic assembly
processes, we obtain homogeneous
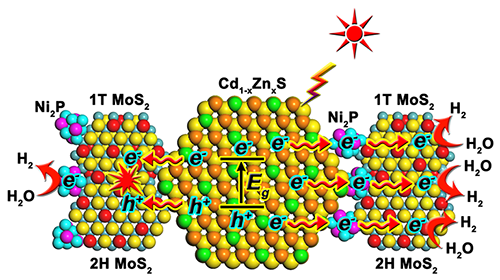
Cd1-xZnxS–Ni2P–MoS2 hybrid nano-spheres consisting of Cd1-xZnxS solid solutions
decorated by Ni2P and 1T/2H MoS2 cocatalysts,
which demonstrate excellent activity and stability for visible-light-responsive
(l > 420 nm) H2 production. Specifically, the Cd1-xZnxS–Ni2P–MoS2 nano-spheres with
2 wt% Ni2P and 0.2 wt% MoS2 (CZ0.7S–2N–0.2M)
exhibit the optimal HER activity of 55.77 mmol∙g-1∙h-1,
about 47 and 32 times more than that of CZ0.7S and Pt–CZ0.7S,
respectively. The outstanding HER performance of Cd1-xZnxS–Ni2P–MoS2 can be ascribed
to the presence of abundant HER active sites in Ni2P nanoparticles
and 1T/2H MoS2 nanosheets as well as the effective transfer and separation of charge carriers. Moreover, the coupling
sequence of cocatalysts in Cd1-xZnxS–Ni2P–MoS2 is found to be critical in the regulation of charge transfer pathways
and thus the resultant photocatalytic efficiency. The results displayed here
could facilitate the engineering of high-performance photocatalysts employing
multi-component cocatalysts for sustainable solar-to-fuel conversion.