Ruiqi Gao, Huan He, Junxian Bai, Lei
Hao,
Rongchen Shen*, Peng Zhang, Youji Li and Xin Li*
The blue cover, together with elements such as blisters, lightning and the sun, highlights the good prospect of this new type of heterojunction as a photocatalytic material. The "S" shaped dragon depicted by the element of water rises from the bottom, implying that the dragon gets water and magically turns water into green hydrogen over organic/inorganic S-type heterojunction photocatalyst under sunlight irradiation.
Simultaneous Photocatalytic Oxygen Production and Hexavalent Chromium Reduction in Ag3PO4/C3N4 S-scheme Heterojunction
Tao Yang, Pengke Deng, Lele Wang, Jie Hu*, Qinqin Liu* and Hua Tang*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2022, 41, 2206023-2206030 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2022-0062
June 20, 2022
S-scheme charge transfer route, Ag3PO4/C3N4, Cr(VI) reduction, O2 production, photocatalysis
ABSTRACT
The low separation/migration efficiency is a major obstacle that limits
the practical application of semiconductor-photocatalysts. Constructing S-scheme
heterojunction is an ideal strategy for providing high photocatalytic activity via
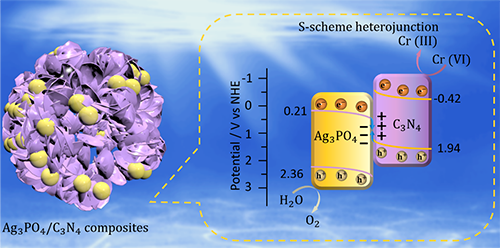
accelerating charge separation. Herein, an Ag3PO4/C3N4 composite was synthesized by coupling Ag3PO4 particle
with C3N4 hollow spheres in-situ via a precipitation method. The S-scheme heterojunction
between Ag3PO4 and C3N4 could accelerate the charge separation and retain high photoredox
ability, which synchronously realized
high photocatalytic oxygen production and hexavalent chromium reduction. The
optimized Ag3PO4/C3N4 composite shows
a high oxygen production rate up to 803.31 µmol·g-1·h-1 and a high conversion (87.9%) of Cr(VI) to Cr(III). In addition, C3N4 hollow spheres affords higher reaction efficiency
than that of C3N4 tube, C3N4 bulk
and C3N4 sheet, which indicates that the hollow sphere
structure can provide more active sites and adsorption sites in the
photocatalytic process. This work offers an effective way in developing a dual-function
S-scheme heterojunction for clean energy production and environmental
protection.