Ruiqi Gao, Huan He, Junxian Bai, Lei
Hao,
Rongchen Shen*, Peng Zhang, Youji Li and Xin Li*
The blue cover, together with elements such as blisters, lightning and the sun, highlights the good prospect of this new type of heterojunction as a photocatalytic material. The "S" shaped dragon depicted by the element of water rises from the bottom, implying that the dragon gets water and magically turns water into green hydrogen over organic/inorganic S-type heterojunction photocatalyst under sunlight irradiation.
Pyrene-Benzothiadiazole-Based Polymer/CdS 2D/2D Organic/Inorganic Hybrid S-scheme Heterojunction for Efficient Photocatalytic H2 Evolution
Ruiqi Gao, Huan He, Junxian Bai, Lei Hao, Rongchen Shen*, Peng Zhang, Youji Li and Xin Li*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2022, 41, 2206031-2206038 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2022-0096
June 20, 2022
photocatalytic hydrogen evolution, pyrene-benzothiadiazole-based conjugated polymers, S-scheme heterojunction, CdS
ABSTRACT
Nowadays,
conjugated polymers have garnered
numerous attention as a new class of organic photocatalysts due to their
tunable electronic properties, low cost, excellent stability and sufficient
light-absorption performance. In particular, pyrene-benzothiadiazole-based
conjugated polymer (PBBP) has been considered to be a new type of conjugated
polymers for photocatalytic H2 evolution. However, the poor charge
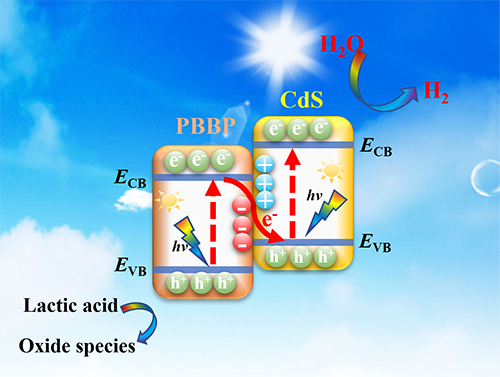
separation seriously limits its practical application in H2 evolution. In this work, a PBBP-based polymer/CdS 2D/2D organic/inorganic
S-scheme heterojunction photocatalyst with a strong internal electric field is, for the first time, prepared for
efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. The pyrene-benzothiadiazole-based
conjugated polymers (PBBP) are synthesized by the Suzuki-Miyaura reactions.
Then, the hybrid heterojunction photocatalysts are fabricated by coupling CdS
with it through the ultrasonic mixing method. As a result, the highest H2-production
rate of 15.83 mmol h-1 g-1 is achieved on 20% PBBP/CdS
composite under visible-light irradiation, nearly 2.7 times higher than that of
pure CdS. The apparent quantum efficiency (AQE) of 20% PBBP/CdS composite could
reach 8.66% at λ = 420 nm. The enhanced activity could be attributed to the
construction of S-scheme heterojunction, which accelerates the recombination of
carriers with weaker redox ability and maintains the strong reducibility of
electrons in CdS. This work provides a protocol for
pyrene-benzothiadiazole-based conjugated polymers to prepare S-scheme
heterojunction photocatalysts based on organic/inorganic coupling.