Ruiqi Gao, Huan He, Junxian Bai, Lei
Hao,
Rongchen Shen*, Peng Zhang, Youji Li and Xin Li*
The blue cover, together with elements such as blisters, lightning and the sun, highlights the good prospect of this new type of heterojunction as a photocatalytic material. The "S" shaped dragon depicted by the element of water rises from the bottom, implying that the dragon gets water and magically turns water into green hydrogen over organic/inorganic S-type heterojunction photocatalyst under sunlight irradiation.
Ag2S Quantum Dots Decorated on Porous Cubic-CdS Nanosheets-Assembled Flowers for Photocatalytic CO2 Reduction
Wei Fu, Jiajie Fan and Quanjun Xiang*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2022, 41, 2206039-2206047 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2022-0090
June 20, 2022
CdS nanosheet, Ag2S quantum dots (QDs), assembled flower structure, composite materials, photocatalytic CO2 reduction
ABSTRACT
The production of renewable fossil fuels such as CH4 and CO by photocatalytic CO2 reduction has attracted more and more
attention. However, single photocatalyst is less efficient for photocatalytic
reduction of CO2 due to the fast recombination of photogenerated
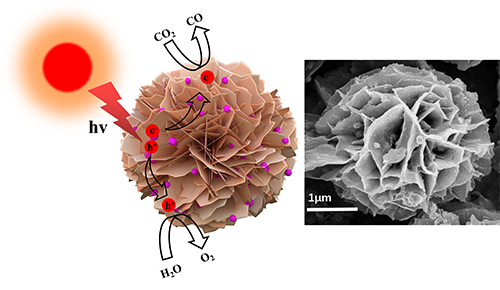
electron pairs. Herein, we successfully prepare CdS-Ag2S composite
by assembling the Ag2S QDs cocatalyst on the surface of CdS
nanosheet-assembled flower through oil-bath solvothermal method. This composite
is prepared through a simple self-assembly strategy using cadmium
chloride, ammonia and thiourea as precursors of the CdS nanosheet-assembled
flower and silver nitrate and 3-mercaptopropionic acid as the precursors of Ag2S
QDs. The average diameter of Ag2S QDs is apparently 6.0 nm. The
light absorption edge of the composite is at around 560 nm, with the
corresponding band gap at 2.14 eV. The
CdS-Ag2S QDs composite with 5 wt% Ag2S QDs loaded achieves
CO evolution rate of 16.6 μmol·g-1·h-1 without
noble-metal cocatalysts. This strengthened photocatalytic performance and
photocatalytic stability were attributed to the energy band broadening of Ag2S
QDs caused by quantum size effect and the large specific surface area due to
the assembled flower. The mechanism underlying the enhanced photocatalytic CO2 reduction activity is further proposed. This study demonstrates that
semiconductor-based quantum dots are strong candidates for excellent
cocatalysts in photocatalysis.