Ruiqi Gao, Huan He, Junxian Bai, Lei
Hao,
Rongchen Shen*, Peng Zhang, Youji Li and Xin Li*
The blue cover, together with elements such as blisters, lightning and the sun, highlights the good prospect of this new type of heterojunction as a photocatalytic material. The "S" shaped dragon depicted by the element of water rises from the bottom, implying that the dragon gets water and magically turns water into green hydrogen over organic/inorganic S-type heterojunction photocatalyst under sunlight irradiation.
Molecular-Level Engineering of S-scheme Heterojunction: the Site-Specific Role for Directional Charge Transfer
Jianjun Zhang, Linxi Wang*, Mitra Mousavi, Jahan B. Ghasemi and Jiaguo Yu
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2022, 41, 2206003-2206005 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2022-0150
June 20, 2022
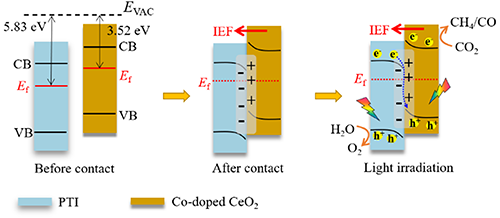
S-scheme heterojunction, functionalized Co-doped regulation, directional electron-driving effect, CO2 photoreduction
ABSTRACT
The
promising S-scheme heterojunction photocatalysts are considered as a novel
frontier due to their superiority in various solar-driven energy-related applications. Recently, a novel
atom-specific tailoring strategy has been introduced on the construction
of S-scheme heterojunction for promoting the electronic transferability. The S-scheme heterojunction is regulated by integrating high-crystalline carbon
nitride with Co-doped
CeO2. Specifically, this atom-specific regulation of S-scheme heterojunction boosts directional electron-driving effect towards functionalized Co sites, benefit-ing for effective photogenerated charge carrier
transferability.
Moreover, a series of tracking
characterizations show that Co-embedded modification promotes CO2 photoreduction into
hydrogenation steps, resulting in high performance towards CO2-to-CH4 photoreduction, which provides new
opportunities for the development of multifunctional cooperation in
heterogeneous photocatalysis.