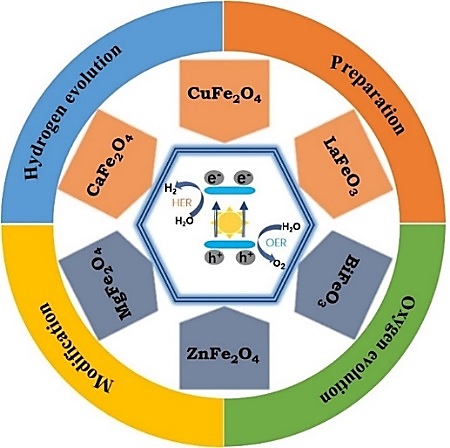
Research Progress of Ferrite Materials for Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting
Yani Wang, Jingwei Huang, Lei Wang, Houde She and Qizhao Wang*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2022, 41, 2201054-2201068 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2021-0020
January 13, 2022
ferrite, photoelectrochemical, water splitting, hydrogen
ABSTRACT
Photoelectrochemical (PEC) water splitting is an
effective strategy to convert solar energy into clean and renewable hydrogen
energy. In order to carry out effective PEC conversion, researchers have
conducted a lot of exploration and developed a variety of semiconductors
suitable for PEC water splitting. Among them, metal oxides stand out due to their
higher stability. Compared with traditional oxide semiconductors, ferrite-based
photoelectrodes have the advantages of low cost, small band gap, and good
stability. Interestingly, due to the unique characteristics of ferrite, most of
them have various tunable features, which will be more conducive to the
development of efficient PEC electrode. However, this complex metal oxide is
also troubled by severe charge recombination and low carrier transport
efficiency, resulting in lower conversion efficiency compared to theoretical
value. Based on this, this article reviews the structure, preparation methods,
characteristics and modification strategies of various common ferrites. In
addition, we analyzed the future research direction of ferrite for PEC water splitting,
and looked forward to the development of more efficient catalysts.