Cover Picture
High thermal conductivity in Ga2TeO6 crystals: Synergistic effects of rigid polyhedral frameworks and stereochemically inert cations
Ziyi Liu, Feifei Guo*, Tingting Cao, Youxuan Sun, Xutang Tao, Zeliang Gao* Submit a Manuscript
High thermal conductivity in Ga2TeO6 crystals: Synergistic effects of rigid polyhedral frameworks and stereochemically inert cations
Ziyi Liu, Feifei Guo*, Tingting Cao, Youxuan Sun, Xutang Tao, Zeliang Gao* Submit a Manuscript
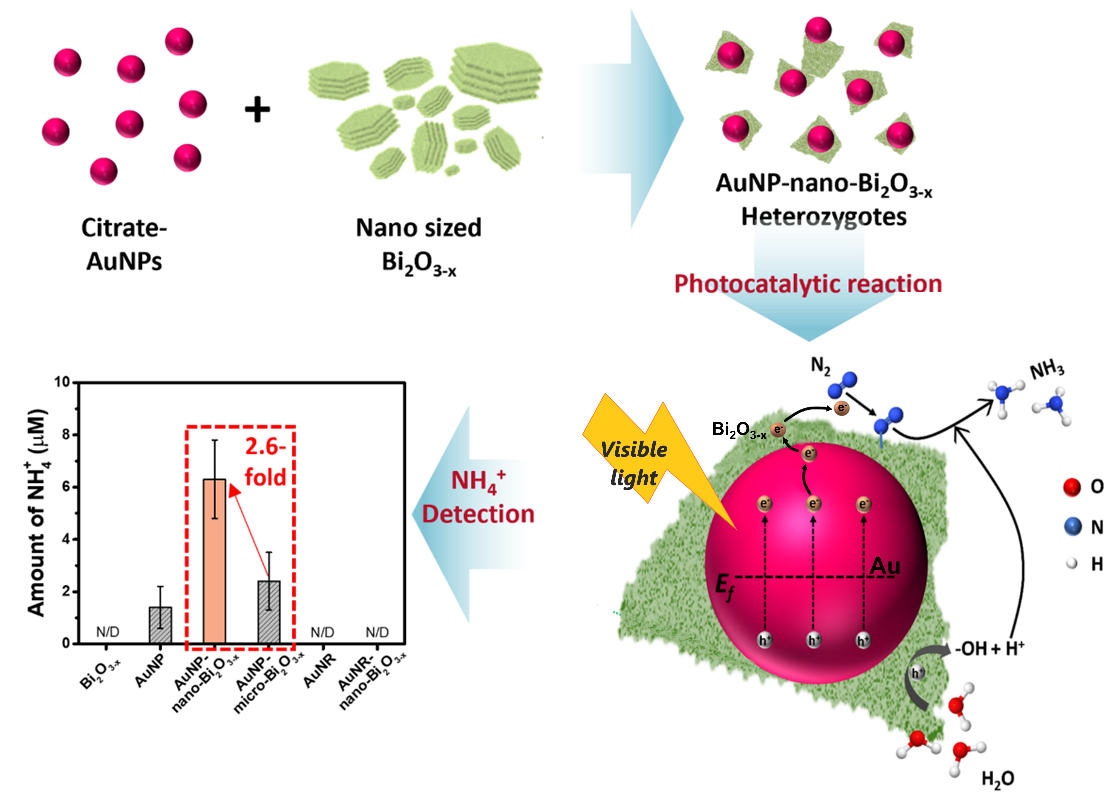
Visible-light responsive gold nanoparticle and nano-sized Bi2O3-x sheet heterozygote structure for efficient photocatalytic conversion of N2 to NH3
Jijoe Samuel Prabagar, Kumbam Lingeshwar Reddy, Dong-Kwon Lim*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem., 2025, 44(4), 100564. DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2025.100564
April 1, 2025
Photocatalyst; Gold nanoparticle; Bismuth oxide; Oxygen vacancy; Nitrogen fixation
ABSTRACT
The advancement in catalysis techniques for sustainable environmental applications, particularly an alternative to the current Haber-Bosch process for NH3, has recently gained widespread attention. Although photocatalytic conversion of N2 to NH3 using solar energy is an eco-friendly method, it has the limitation of low quantum yield. Recently, 2D Bi-based photocatalysts which exhibit higher visible light absorption than TiO2 and higher stability than MXene have been an active research topic, and their performance can be enhanced through improved visible light absorption properties by incorporating plasmonic gold nanoparticles while nitrogen adsorption could be enhanced through oxygen vacancy (OV) processes. In the present study, we explore the application of 2D nano-sized Bi2O3–x and gold nanoparticles for visible light photo generation of NH3. HRTEM and XPS reveal that the formation of AuNP and nano-sized Bi2O3–x in AuNP/Bi2O3–x heterozygote structure promotes the charge carrier mobility and charge transport at the interface, resulting in a 2.6-fold increase in the photocatalytic activity compared to micro-sized Bi2O3–x with AuNP. The improved photocatalytic performance can be ascribed to significant enhancement of visible light absorption by plasmonic nanoparticles, fast charge transport and mobility (due to sheet morphology) and the N2 activation by OV in AuNP/Bi2O3–x heterozygote. Through a systematic experimental investigation involving catalysts, concentration, pH, and scavengers, the highest photocatalytic performance was achieved with the heterozygote structures of AuNP/n-Bi2O3–x under optimized conditions, yielding 432.5 μmol gcat−1 h−1 of NH3.