Cover Picture
P-Ni4Mo Catalyst for Seawater Electrolysis with High Current Density and Durability
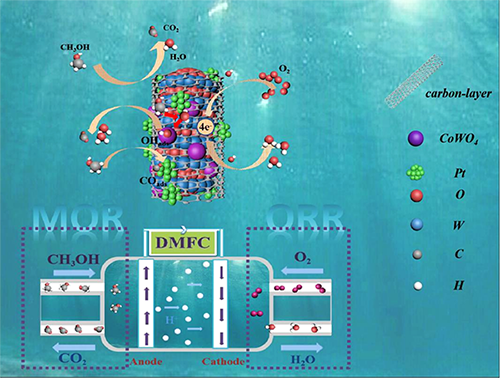
Acid-Stable CoWO4/WO3-Microrod Coated by a Thin Carbon-Layer as Efficient Pt Co-Catalysts for Methanol Oxidation and Oxygen Reduction
Jiahuan Li, Jiahao Xie, Xinyu Wang, Ying Dai*, Xiaoqin Xu, Jin Liu, Zhuang Cai*, Xin Meng and Jinlong Zou*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2022, 41, 2207059-2207067 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2022-0104
July 18, 2022
acid resistance, methanol-tolerance, oxygen vacancies, strong metal-support interaction, thin carbon-layer
ABSTRACT
Insufficient
activity and instability (poisoning) of Pt-based electrocatalysts for
methanol oxidation and oxygen reduction reactions (MOR/ORR) impede the
development of direct methanol
fuel cells. Here, CoWO4 nanoparticles-loaded WO3 microrods coated by a thin carbon-layer are used as Pt-supports/co-catalysts
for MOR/ORR. WO3 grows along the (110) crystal plane to form
microrod (diameter of ~0.6 um),
which is coated by a carbon-layer (~5 nm). Pt-CoWO4/WO3@NCL-mr (850 ℃) shows a higher mass activity (2208 mA mg-1pt)
than the commercial Pt/C
(659.4 mA mg-1pt). CoWO4/WO3 heterojunction on the microrod surface
with abundant oxygen vacancies allows the generation of surface-adsorbed
hydroxyl to facilitate CO elimination and regeneration of the occupied Pt
active-sites (promising stability). Pt-CoWO4/WO3@NCL-mr
(850 ℃) has higher half-wave (0.46 V) and onset (0.54 V)
potentials than Pt/C (0.41 and 0.50 V) for ORR. The microrod structure of CoWO4/WO3@NCL facilitates the dispersibility of Pt NPs to
increase the utilization of Pt active sites and relieve the self-aggregation of
Pt to obtain a promising synergy between Pt and CoWO4 (Co2+) for ORR in acid media. This
study provides insights not only into the synthesis of acid-resistant WO3@NCL
microrod as active Pt co-catalyst, but also into the effective
utilization of surface oxygen
vacancies and Co2+ for MOR/ORR.