Cover Picture
Unraveling the Dynamic
Structural Evolution of Phthalocyanine Catalysts during CO2 Electroreduction
Jianing Mao, Bingbao Mei*, Ji Li, Shuai Yang, Fanfei Sun,
Siyu Lu, Wei Chen, Fei Song* and Zheng
Jiang*
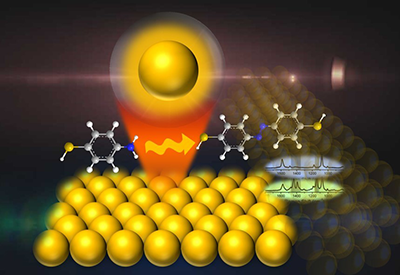
Phthalocyanine catalysts have well-defined active site structures that allow reaction-based mechanism exploration. In this regard, the actual behaviors of metal ions in the phthalocyanine catalysts have aroused considerable attention. Operando high-energy resolution fluorescence detected X-ray absorption (HERFD-XANES) can be employed in the practical situation of electrocatalysis to realize the interfacial interaction between metal ions and the reactants, offering a unique insight into the active site geometry and structural evolution during CO2 reduction. In this work, the CO2RR to CO dominates over the HER with Faradaic efficiency reaching the maximum value of 89% at 0.85 V versus RHE. The results demonstrate the atomically dispersed, low-valent Ni(I) centres with high intrinsic CO2 reduction activity.
Submit a ManuscriptWumei Cao, Yang Lu and Yi-Fan Huang*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2022, 41, 2210077-2210081 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2022-0134
October 25, 2022
surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy, p-aminothiophenol, temperature, plasmon-mediated chemical reaction
ABSTRACT