Cover Picture
Ir/Ni–N–C electrocatalyst with promoted CO-tolerance towards alkaline hydrogen oxidation reaction
Yiming Jin, Mingming Pan, and Wei Luo* Submit a Manuscript
Ir/Ni–N–C electrocatalyst with promoted CO-tolerance towards alkaline hydrogen oxidation reaction
Yiming Jin, Mingming Pan, and Wei Luo* Submit a Manuscript
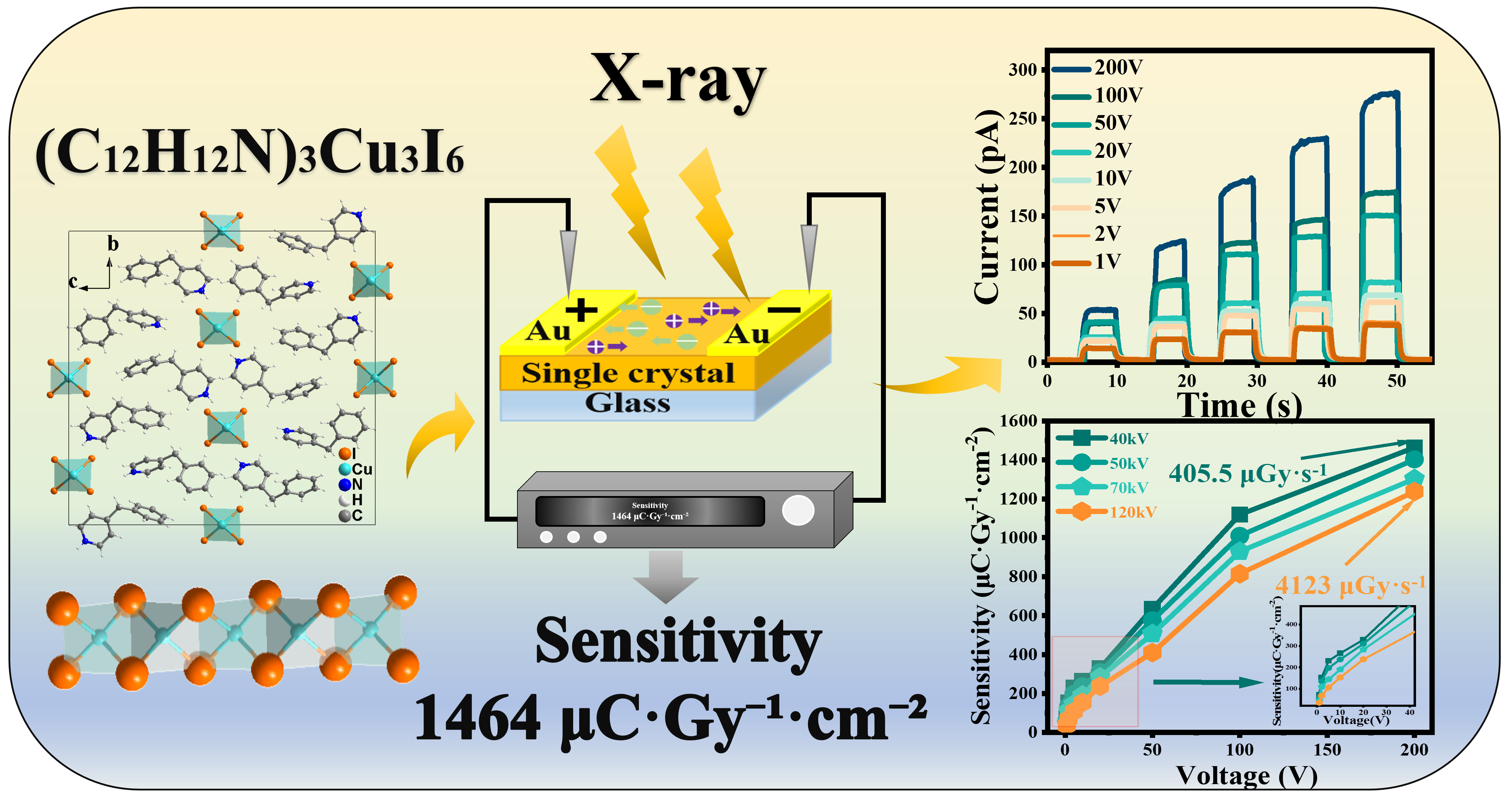
One-dimensional (C12H12N)3Cu3I6 for high-performance direct X-ray detection
Pan Gao, Qingzheng Kong, Ying Sun, Qian Ma, Qi Wang, Zeyu Guo, Ledi Li, Bingbing Li, Jingwei Xu, Xiaomei Jiang*, Zhaolai Chen
Chin. J. Struct. Chem., 2026, 45(1), 100767. DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2025.100767
January 1, 2026
Organic copper halides; One-dimensional structure; X-ray detection; X-ray imaging
ABSTRACT
X-ray detectors, as crucial elements in medical imaging and industrial fields, can be categorized into direct and indirect types. Direct detectors, which directly convert X-ray photons into electrical signals, exhibit high sensitivity and low detection limits, enabling the capture of high-resolution images and reducing radiation exposure to patients. Organic copper halides, recognized as potential active materials for X-ray detection, have been widely explored in the indirect scintillation field but remain under-explored in direct X-ray detector applications. In this work, (C12H12N)3Cu3I6 is demonstrated as an efficient semiconductor for direct X-ray detection with excellent stability. A lateral-structured X-ray detector was fabricated with gold electrodes, which exhibits a maximum sensitivity of 1464.14 μC·Gy-1·cm-2, a lowest detection limit of 19.8 nGy·s-1, a high on-off ratio of 2140, and an excellent operational stability of retaining 96% performance after 600 s continuous X-ray radiation. Furthermore, the detector successfully imaged a 0.1 mm “F”-shaped lead sheet, validating its capacity for X-ray imaging. This study highlights the potential of (C12H12N)3Cu3I6 as a promising semiconductor for high-performance direct X-ray detection, expanding the application scope of organic copper halides in this critical field.