Just Accepted
Just Accepted Articles have been posted online after technical editing and typesetting for immediate view. The final edited version with page numbers will appear in the Current Issue soon.
Submit a Manuscript

Quasi-one-dimensional antimony selenide photocathodes: From fundamentals to future direction
Ziying Zhang, Xiangjiu Guan*, and Liejin Guo*
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjsc.2026.100864
Antimony selenide; Quasi-one-dimensional; Photoelectrochemistry; Interface engineering; Solar-to-fuel
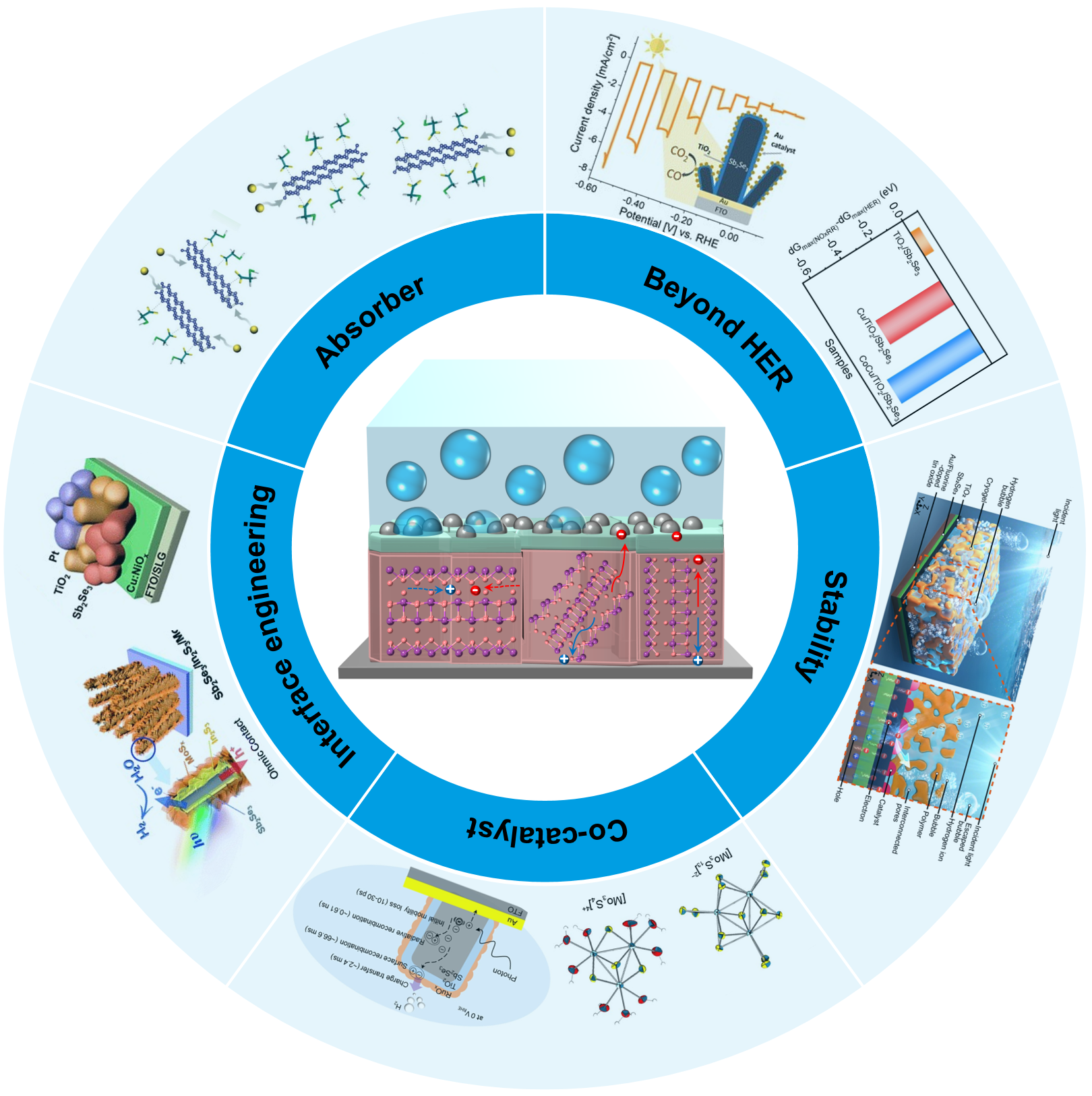
ABSTRACT
Antimony selenide (Sb2Se3) has emerged as a promising absorbing material in photocathode for photoelectrochemical (PEC) hydrogen evolution, exhibiting a development trajectory that outpaces many traditional semiconductors. Despite growing research interest, few reviews have provided a comprehensive roadmap for this class of photocathodes. In this review, starting from the scope and fundamentals of PEC systems, we will introduce how the quasi-one-dimensional (1D) crystal structure of Sb2Se3 enables anisotropic carrier transport, benign grain boundaries, and intrinsic stability. Advances in both vacuum and solution-based deposition techniques have yielded high-quality and scalable thin films, while recent progress in crystal orientation control, interface engineering, and co-catalyst integration has markedly improved efficiency. In parallel, the application of protection layers and bubble management strategies has extended operational stability. Beyond hydrogen evolution, Sb2Se3 has also shown potential for alternative solar-driven reactions. Nevertheless, challenges such as defect-induced recombination, interfacial mismatches, and long-term durability remain critical bottlenecks. Future progress will rely on integrated efforts in interface engineering, defect and crystal quality control, advanced protection and bubble management strategies, and the development of earth-abundant co-catalysts for alternative reactions, thereby linking fundamental material optimization with practical device deployment in solar-to-fuel technologies.