Graphene Oxide/Fe3O4 Magnetic Nanocomposites for Efficient Recovery of Indium
WANG Ling-Hang, QIU Zhi-Hua and CHI Li-Sheng*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2021, 40, 1423-1432 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-3161
December 15, 2021
adsorbent, graphene oxide, Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles (NPs), nanocomposites, In(Ⅲ)
ABSTRACT
Adsorbent has been widely
used for the recovery and enrichment of rare metals from waste water. Herein, a
graphene-based adsorbent, graphene oxide/Fe3O4 (GO/Fe3O4)
nanocomposite, was prepared by a facile hydrothermal method, and characterized
by X-ray diffraction, Scanning Electron Microscope, X-ray
Photoelectron Spectroscopy, Zeta
potential and magnetization. The material has
been explored for the recovery of In from simulated waste water. The
test results show that the nanocomposite has a reasonable adsorption
capacity on indium in a wide pH range, e.g., the adsorption percent and
quantity of In(Ⅲ) from the aqueous solutions at pH = 4 and C0 = 50
mg·L−1 are 91% and 43.98 mg·L−1, respectively. In
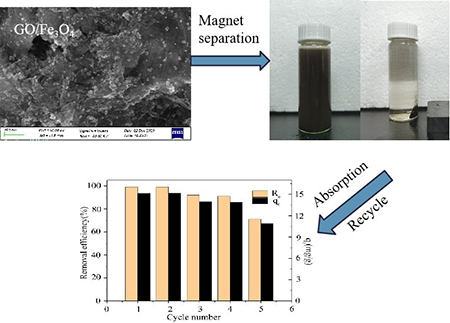
addition, the nanocomposites maintain a 75.5% cycling capacity and a 71%
removal efficiency after five continuous cycles due to their novel properties of
high specific surface area and superparamagnetism. The pseudo-second-order adsorption model can be used to interpret the
kinetic data. High adsorption efficiency and good reusability can make the
nanocomposite a promising adsorbent for recovery of In(Ⅲ).