Synthesis, Characterization, Biological and Docking Simulations of 4-(Benzylideneamino) Benzoic Acids
HAMID Aziz, AAMER Saeed*, FARUKH Jabeen, ABDUL Basit, IRFAN Zia Qureshi, ABDUL Aziz, ATIF Haroon and ASHFAQ Ur Rehman
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2021, 40, 291-300 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-2871
March 15, 2021
antidiabetic, biochemical, cholesterol, glibenclamide, simulations
ABSTRACT
The present research paper presents the synthesis, characterization, biological and computational studies
of 4-(benzylideneamino) benzoic acid derivatives (3a~3g). Derivatives 3a~3c displayed best antidiabetic potential with a
glucose-lowering effect compared to the reference drug Glibenclamide.
Biochemical parameters including plasma glucose, serum triglycerides,
cholesterol, alanine amino transferase and aspartate amino transferase levels
showed significant alterations in concentrations relative to the control. Similarly,
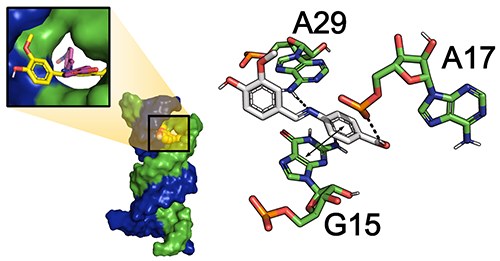
the derivatives 3a, 3d and 3e displayed potent in vitro antibacterial potential. Molecular docking simulations delineated that the
ligands and complexes were stabilized at the active site by electrostatic and
hydrophobic forces, consistent with the corresponding experimental results. In
silico study of the binding pattern predicted that the synthesized ligands, 3d and 3a could serve as a potential surrogate for hit-to-lead generation and the
design of novel antibacterial drugs.