A New Manganese Coordination Polymer Based on Azobenzene Tetracarboxylate and Auxiliary Pyridine Ligand: Synthesis, Crystal Structure and Magnetic Property
FENG Xun*, SHANG Ya-Pei, WANG Li-Ya, HONG Man-Zhou, FANG Hai-Peng, ZHAO Xin and LI Zhong-Jun
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2021, 40, 217-224 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2011-2809
February 15, 2021
acetate bridging, manganese(II), X-ray crystal structure, oxidation azoxybenzene-2,2΄,3,3΄-tetra- carboxyl acid, antiferromagnetic interaction
ABSTRACT
A new manganese coordination polymer (CP) has been
synthesized under hydrothermal conditions. It’s formula is {Mn2(Oaobtc)(bpe)(H2O)4]}n,
where H4Oobtc represents oxide azobenzene 2,2΄,3,3΄-tetracarboxyl acid,
and bpe is 1,2-bis(4-pyridine) ethylene. It was characterized by elemental
analysis, infrared spectrum and X-ray single-crystal diffraction. The
coordination polymer crystallizes in the monoclinic system, space group P21/c. The central ion was coordinated with H4Oobtc ligands
using bridging model, and carboxylic group connects two adjacent Mn(II) ions into dimer units. The oxygen
from carboxylates connect these dimer units into a one-dimensional (1D) chain, and N atoms from the
bpe further expanded them into three-dimensional (3D) supramolecular
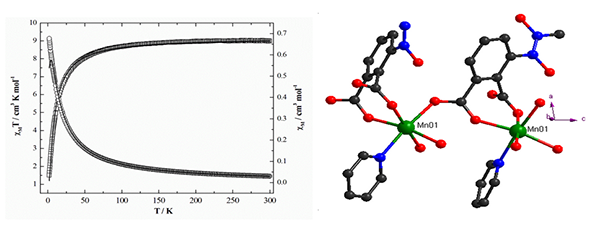
edifice, eventually. Variable-temperature magnetic measurements of CP 1 indicate the
presence of weak antiferromagnetic exchange between two nearest Mn(II) ions with J = –0.367 cm-1.