Ruiqi Gao, Huan He, Junxian Bai, Lei
Hao,
Rongchen Shen*, Peng Zhang, Youji Li and Xin Li*
The blue cover, together with elements such as blisters, lightning and the sun, highlights the good prospect of this new type of heterojunction as a photocatalytic material. The "S" shaped dragon depicted by the element of water rises from the bottom, implying that the dragon gets water and magically turns water into green hydrogen over organic/inorganic S-type heterojunction photocatalyst under sunlight irradiation.
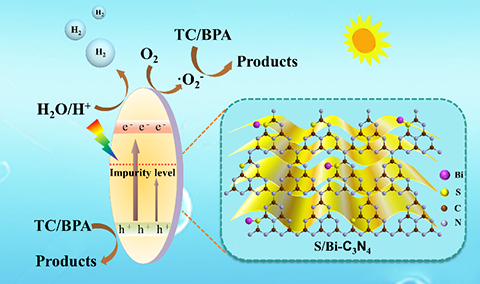
Bi and S Co-doping g-C3N4 to Enhance Internal Electric Field for Robust Photocatalytic Degradation and H2 Production
Yan Hu, Xibao Li*, Weiwei Wang, Fang Deng*, Lu Han*, Xiaoming Gao, Zhijun Feng, Zhi Chen, Juntong Huang, Fanyan Zeng and Fan Dong
Chin. J. Struct. Chem. 2022, 41, 2206069-2206078 DOI: 10.14102/j.cnki.0254-5861.2022-0103
June 20, 2022
photocatalysis, g-C3N4, co-doping, IEF strength, antibiotic
ABSTRACT
By
adjusting the type and proportion of doping elements in the g-C3N4-based
photocatalyst, the internal electric field (IEF) strength of the semiconductor
can be regulated. This can effectively enhance the driving force of charge
separation in the photocatalytic process. It is found that the introduction of
appropriate concentration of Bi and S into the skeleton structure of g-C3N4 can achieve efficient degradation of tetracycline
(TC) and other pollutants in the liquid environment and excellent
photocatalytic H2 evolution performance (1139 μmol·L-1·h-1).
Since the prepared samples have similar crystal structures, the relative
strength of IEF can be calculated. It can be used as the basis for adjusting
the IEF strength of g-C3N4-based semiconductor by element
doping. In addition, the Bi and S co-doped g-C3N4 samples
after solvothermal reflux show good chemical stability and can reduce the
nanostructure defects caused by co-doping of heteroatoms, thus it provides a
novel solution for the construction of g-C3N4-based
dual-function photocatalyst with high activity and stability.