Cover Picture
Ir/Ni–N–C electrocatalyst with promoted CO-tolerance towards alkaline hydrogen oxidation reaction
Yiming Jin, Mingming Pan, and Wei Luo* Submit a Manuscript
Ir/Ni–N–C electrocatalyst with promoted CO-tolerance towards alkaline hydrogen oxidation reaction
Yiming Jin, Mingming Pan, and Wei Luo* Submit a Manuscript
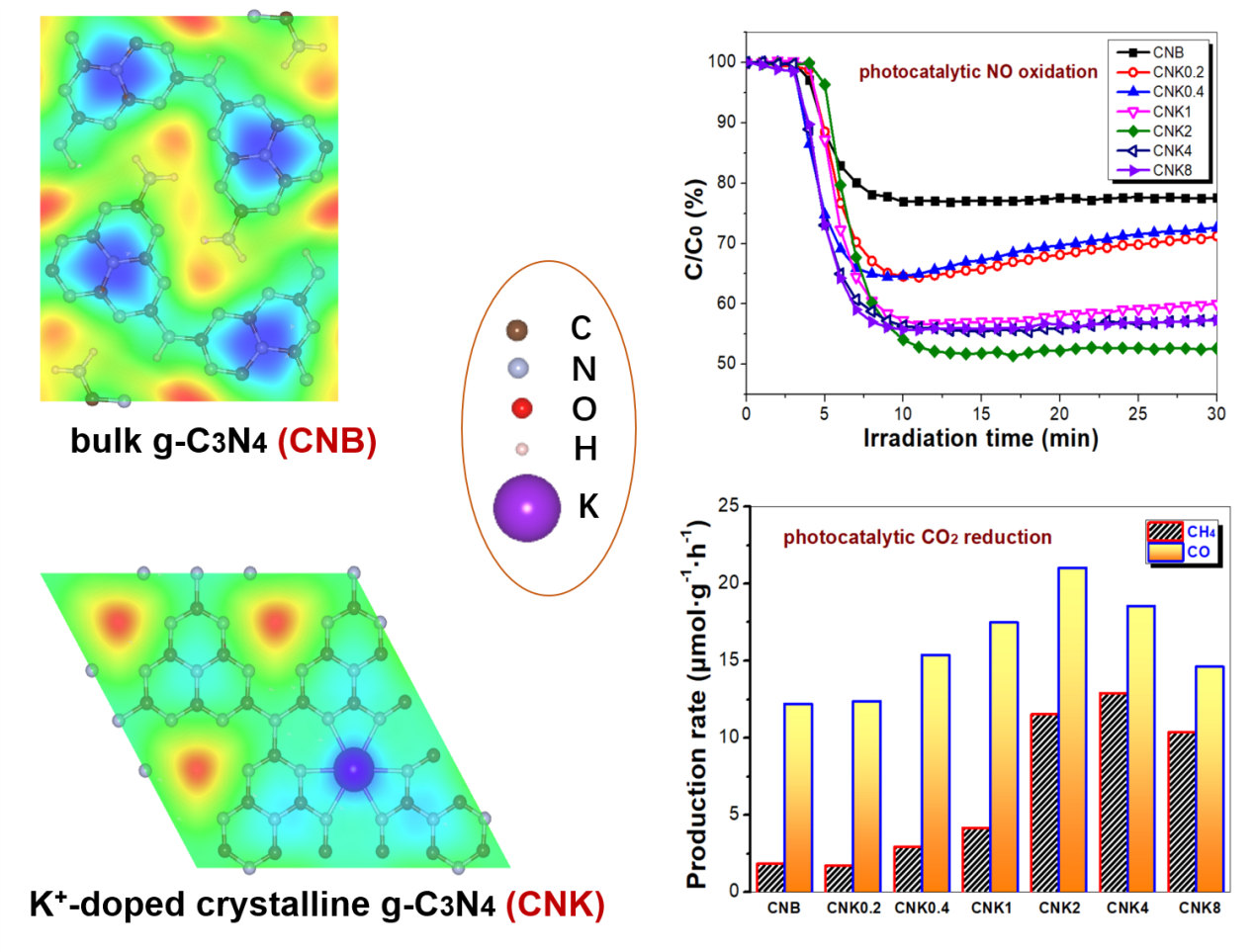
Enhancing the photocatalytic activity of crystalline g-C3N4 towards NO oxidation and CO2 reduction through K+-doping and cyano defect engineering
Zhou Li, Mengxue Yu, Shixin Chang, Zhibin Huang, Zhenmin Cheng, Weibin Zhang, Sónia A.C. Carabineiro, Zhigao Xu, Kangle Lv*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem., 2026, 45(1), 100698. DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2025.100698
January 1, 2026
Crystalline g-C3N4; Build-in electric field; Photocatalysis; NO oxidation; CO2 reduction
ABSTRACT
The polymeric semiconductor photocatalyst graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) has attracted considerable attention due to its visible-light responsiveness and excellent biocompatibility. However, the photocatalytic efficiency of bulk g-C3N4 (CNB) remains insufficient for pratical applications, primarily due to its limited light absorption range and the rapid charge carrier recombination. In this study, K+-doped crystalline g-C3N4 with cyano defects (CNK) was synthesized by the calcination of dicyandiamide in the presence of KCl. The addition of KCl promoted the formation of K+-doped crystalline g-C3N4 with cyano defects. The optimized photocatalyst (CNK2) exhibited the highest photocatalytic activity for NO oxidation, achieving a removal rate of 47.40%, which is 2.1 times higher than that of CNB. This enhancement is mainly attributed to the increased generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), particularly superoxide radicals (•O2-) and singlet oxygen (1O2). Furthermore, improved performance in photocatalytic CO2-to-CH4 conversion was also observed, which is attributed to the formation of a build-in electric field (BIEF) induced by K+ ion doping and the introduction of cyano defects.