Cover Picture
Ir/Ni–N–C electrocatalyst with promoted CO-tolerance towards alkaline hydrogen oxidation reaction
Yiming Jin, Mingming Pan, and Wei Luo* Submit a Manuscript
Ir/Ni–N–C electrocatalyst with promoted CO-tolerance towards alkaline hydrogen oxidation reaction
Yiming Jin, Mingming Pan, and Wei Luo* Submit a Manuscript
Ir/Ni-N-C electrocatalyst with promoted CO-tolerance towards alkaline hydrogen oxidation reaction
Yiming Jin, Mingming Pan, Wei Luo*
Chin. J. Struct. Chem., 2026, 45(1), 100760. DOI: 10.1016/j.cjsc.2025.100760
January 1, 2026
Alkaline hydrogen oxidation; CO-tolerance; Hydroxyl binding energy; Intrinsic activity; Single atom supports
ABSTRACT
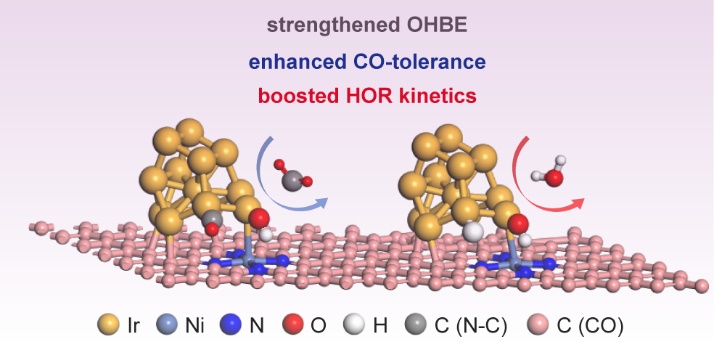
Addressing the CO-sensitive and catalytic efficiency issues of noble metal-based electrocatalysts towards alkaline hydrogen oxidation reaction (HOR) are indispensable for the practical commercialization of advanced anion exchange membrane fuel cells (AEMFCs). Here, Ni-N-C supported Ir catalysts denoted as Ir/Ni-N-C have been constructed and demonstrated greatly improved resistance towards CO impurities compared to conventional N-C or pure C anchored Ir nanoparticles after long-term CO poisoning. Besides, Ir/Ni-N-C possesses superior specific and mass activity of 0.557 mA cm-2 and 1.15 mA mgPGM-1, which is approximately 2-times higher than that of Ir/C and even outperforms the state-of-the-art commercial Pt/C catalysts. Combining in-situ surface-enhanced infrared absorption spectroscopy and density functional calculation, the band structure modulation and coordination effect of Ni-N-C supports lead to strengthened hydroxyl binding energy, promoted CO oxidative desorption under working potential, and lowered activation barrier of the rate-determining process of alkaline HOR. This work sheds light on the importance of metal-N-C substrates for solving the CO-tolerance and intrinsic activity challenges, provides new insights for noble-metal based catalysts designing.